What is mRNA? The messenger molecule that’s been in every living cell for billions of years is the key ingredient in some COVID-19 vaccines
One surprising star of the coronavirus pandemic response has been the molecule called mRNA. It’s the key ingredient in the Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna COVID-19 vaccines. Now it’s even at the heart of the 2023 Nobel Prize in physiology or medicine, which will go to Katalin Karikó and Drew Weissman.
But mRNA itself is not a new invention from the lab. It evolved billions of years ago and is naturally found in every cell in your body. Scientists think RNA originated in the earliest life forms, even before DNA existed.
Here’s a crash course in just what mRNA is and the important job it does.
Meet the genetic middleman
You probably know about DNA. It’s the molecule that contains all of your genes spelled out in a four-letter code – A, C, G and T.
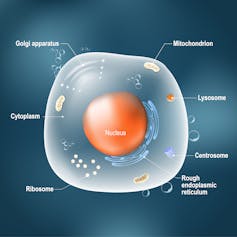
DNA is found inside the cells of every living thing. It’s protected in a part of the cell called the nucleus. The genes are the details in the DNA blueprint for all the physical characteristics that make you uniquely you.
But the information from your genes has to get from the DNA in the nucleus out to the main part of the cell – the cytoplasm – where proteins are assembled. Cells rely on proteins to carry out the many processes necessary for the body to function. That’s where messenger RNA, or mRNA for short, comes in.
Sections of the DNA code are transcribed into shortened messages that are instructions for making proteins. These messages – the mRNA – are transported out to the main part of the cell. Once the mRNA arrives, the cell can produce particular proteins from these instructions.
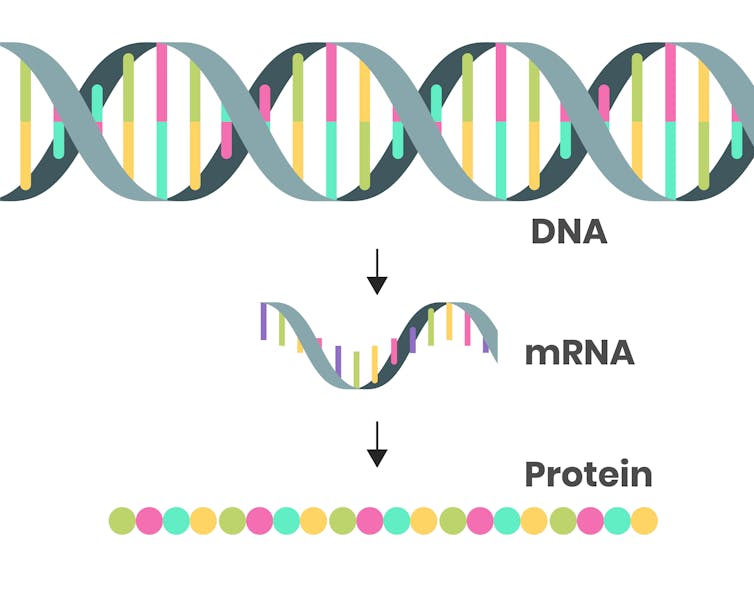
The structure of RNA is similar to DNA but has some important differences. RNA is a single strand of code letters (nucleotides), while DNA is double-stranded. The RNA code contains a U instead of a T – uracil instead of thymine. Both RNA and DNA structures have a backbone made of sugar and phosphate molecules, but RNA’s sugar is ribose and DNA’s is deoxyribose. DNA’s sugar contains one less oxygen atom, and this difference is reflected in their names: DNA is the nickname for deoxyribonucleic acid, RNA is ribonucleic acid.
Identical copies of DNA reside in every single cell of an organism, from a lung cell to a muscle cell to a neuron. RNA is produced as needed in response to the dynamic cellular environment and the immediate needs of the body. It’s mRNA’s job to help fire up the cellular machinery to build the proteins, as encoded by the DNA, that are appropriate for that time and place.
The process that converts DNA to mRNA to protein is the foundation for how the cell functions.
Programmed to self-destruct
As the intermediary messenger, mRNA is an important safety mechanism in the cell. It prevents invaders from hijacking the cellular machinery to produce foreign proteins because any RNA outside of the cell is instantaneously targeted for destruction by enzymes called RNases. When these enzymes recognize the structure and the U in the RNA code, they erase the message, protecting the cell from false instructions.
The mRNA also gives the cell a way to control the rate of protein production – turning the blueprints “on” or “off” as needed. No cell wants to produce every protein described in your whole genome all at once.
Messenger RNA instructions are timed to self-destruct, like a disappearing text or Snapchat message. Structural features of the mRNA – the U in the code, its single-stranded shape, ribose sugar and its specific sequence – ensure that the mRNA has a short half-life. These features combine to enable the message to be “read,” translated into proteins and then quickly destroyed – within minutes for certain proteins that need to be tightly controlled or up to a few hours for others.
Once the instructions vanish, protein production stops until the protein factories receive a new message.
Harnessing mRNA for vaccination
All of mRNA’s characteristics made it of great interest to vaccine developers. The goal of a vaccine is to get your immune system to react to a harmless version or part of a germ so when you encounter the real thing you’re ready to fight it off. Researchers found a way to introduce and protect an mRNA message with the code for a portion of the spike protein on the SARS-CoV-2 virus’s surface.
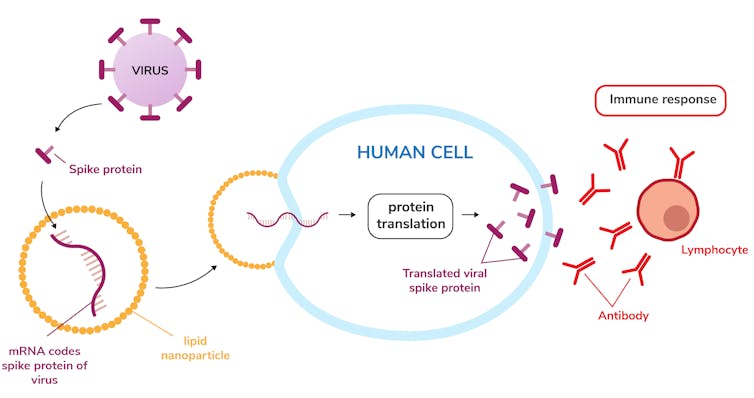
The vaccine provides just enough mRNA to make just enough of the spike protein for a person’s immune system to generate antibodies that protect them if they are later exposed to the virus. The mRNA in the vaccine is soon destroyed by the cell – just as any other mRNA would be. The mRNA cannot get into the cell nucleus, and it cannot affect a person’s DNA.
The first publicly available mRNA vaccines were authorized for emergency use to provide protection against COVID-19 in December 2020 by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. The Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine (Comirnaty) achieved full FDA approval in August 2021, and the Moderna vaccine (Spikevax) received approval in January 2022.
These vaccines were considered brand new in 2020, but the underlying technology had been developed years before and improved incrementally over time. With knowledge from past research, rapid volunteer trials and data collected in real time – from more than 655 million COVID-19 vaccine doses administered in the United States by the end of 2022 – these vaccines were well tested for safety and effectiveness.![]()
Penny Riggs, Associate Professor of Functional Genomics, Texas A&M University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.

